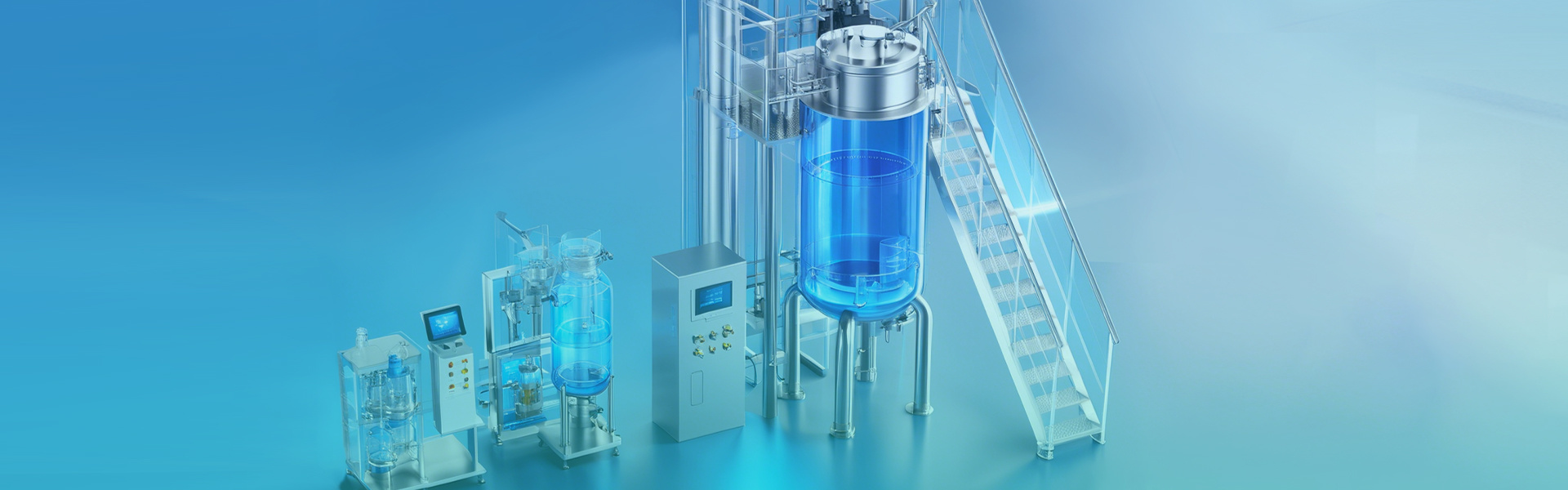
Phototrophic bacteria fermenter: How to use phototrophic bacteria
Release Time:
2021-08-27
Photosynthetic Bacteria Fermenter: How to Use Photosynthetic Bacteria
1. Use judiciously. When using, mix 2-5g/m3 of photosynthetic bacteria evenly with fine dry dung and spread it into the pond. Then, every 20 days or so, add 1-2g/m3 of water and spread it over the entire pond; When using shrimp and crab ponds, use 5-10g/m3 mixed with fine dry fertile mud and spread it evenly in the pond. Then, every 20 days or so, add 2-5g/m3 of water and spread it over the entire pond; When adding photosynthetic bacteria to feed (fish, shrimp, crab), it can be mixed at a ratio of 1%, and fed every 2-3 days; When used for disease prevention, it can be used frequently. The application amount for fish ponds is 1-2g/m3, and the application amount for shrimp and crab ponds is 5-10g/m3. The method is to spread it over the entire pond after adding water.
2. Use it at the right time. Choose to use it on sunny days. The suitable water temperature for using photosynthetic bacteria is above 20℃, and it is not suitable for low-temperature rainy weather.
3. Consider the water's purpose. Using photosynthetic bacteria in fertilized water can promote the transformation of organic pollutants, avoid the accumulation of harmful substances, improve the water environment, and increase biological bait. When the water body is thin, fertilize first to improve the water quality, then apply photosynthetic bacteria, which is conducive to maintaining the vitality and reproductive advantage of photosynthetic bacteria in the water body, and reducing the cost of use. In addition, when the pond water is acidic, slaked lime should be used to adjust the pH value to 7.0-8.0, and then photosynthetic bacteria should be added.
4. Combine with fertilizer. In ponds, the effect of using photosynthetic bacteria with fertilization is more obvious. This can avoid the shortcomings of difficult-to-control water quality due to excessive fertilization, and prevent water quality deterioration caused by algae aging, which is beneficial to enhancing the effects of water body aquaculture and purification.
Photosynthetic Bacteria Fermenter: Cultivation of Photosynthetic Bacteria
The production of photosynthetic bacteria fermenters first involves stirring. In the cultivation of photosynthetic bacteria, keeping the bacterial solution dynamic is beneficial for bacterial cells to float and obtain light, promoting good bacterial cell growth. Practice has proved that the concentration of dynamically cultured bacterial solution is higher than that of statically cultured bacterial solution. Usually, artificial periodic stirring or a sealed circulating pump is used to make the culture solution circulate slowly. Then, by adjusting the light, most photosynthetic bacteria use near-infrared light of 700-900 nanometers, which can be met by ordinary light bulbs of 25-60 watts. Different light intensities and different strain requirements are generally adjusted by controlling the distance between the bulb and the strain level, usually controlled at 15-25cm. Of course, sunlight is the best and cost-free. Temperature adjustment: Generally speaking, the optimal cultivation temperature range for strains is 25-34℃ (adaptation range is 15-40℃). When the temperature is below 15℃, the growth is slow, the bacterial solution color becomes darker, and the precipitation increases. Then, measure the pH value, because bacteria have to use organic acids in the culture solution during the cultivation process, which causes the pH value to rise. Therefore, the pH value should be measured at least once or twice a day. At the beginning, it can be measured once a day, and then increased once every few days. Then, in the biological control of pests and diseases, the main preventive measures are to select clean water and sterilize it strictly. Select high-quality strains. Aging photosynthetic bacteria have poor activity and many harmful metabolic products in the bacterial solution. Then select strains with high concentration, strong activity, few miscellaneous bacteria, and bright purplish-red bacterial solution. Advantageous inoculation amount, maintaining numerical advantage. In large-scale production, due to the inability to eliminate mixed bacteria from water sources, containers, and air, the inoculation amount should be increased to make photosynthetic bacteria have an absolute advantage, thereby cultivating high-quality bacterial solution. Finally, when the photosynthetic bacteria content is high, it can also release bacteriostatic enzymes to inhibit the growth of some miscellaneous bacteria. Practice has proved that the normal inoculation amount for productive cultivation should not be less than 1:5, that is, 1 strain (3 billion level) and 5 culture solutions; when the inoculation conditions are poor, the inoculation amount should not be less than 1:1. Selecting a suitable culture medium is also an important measure to maintain numerical advantage.
Latest News
2025-07-28
The 15th Shanghai International Bio-fermentation Products and Technology Equipment Exhibition 2025 will be grandly held at the Shanghai New International Expo Center from August 7th to 9th.
How can the fermentation system be upgraded?
2022-05-13
Fermentation systems are commonly used in research, production, seed production, and large-scale factory production units for liquid strains. They are also used in the cultivation of various microorganisms, the production of food containing edible fungal active ingredients, and the production of active factors in various dairy products. Therefore, its application range is very wide, commonly used in mycelia.
What are the disadvantages of laboratory fermenters?
2022-04-27
Laboratory fermenters are mainly used in research, production, seed production, and large-scale production units of liquid strains, and are also used in the cultivation of various microorganisms, the production of food containing edible fungus active ingredients, and the production of active factors in various dairy products. Therefore, its application range is very wide, usually in mycelia.
How is the fermentation system managed?
2022-04-21
Fermentation systems are used in the production of food and various dairy products' active factors, so their application is very widespread. Commonly used in mycelia, extracting bioactive ingredients to produce various food additives, extracting bioactive ingredients to produce various food additives, in microbial engineering it is used to produce pesticides, pharmaceuticals, hormones, etc., suitable for scientific research units, and mushroom companies.