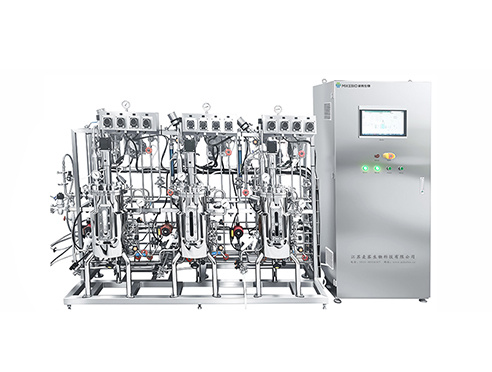
A brief introduction to bioreactors
Release Time:
2021-09-05
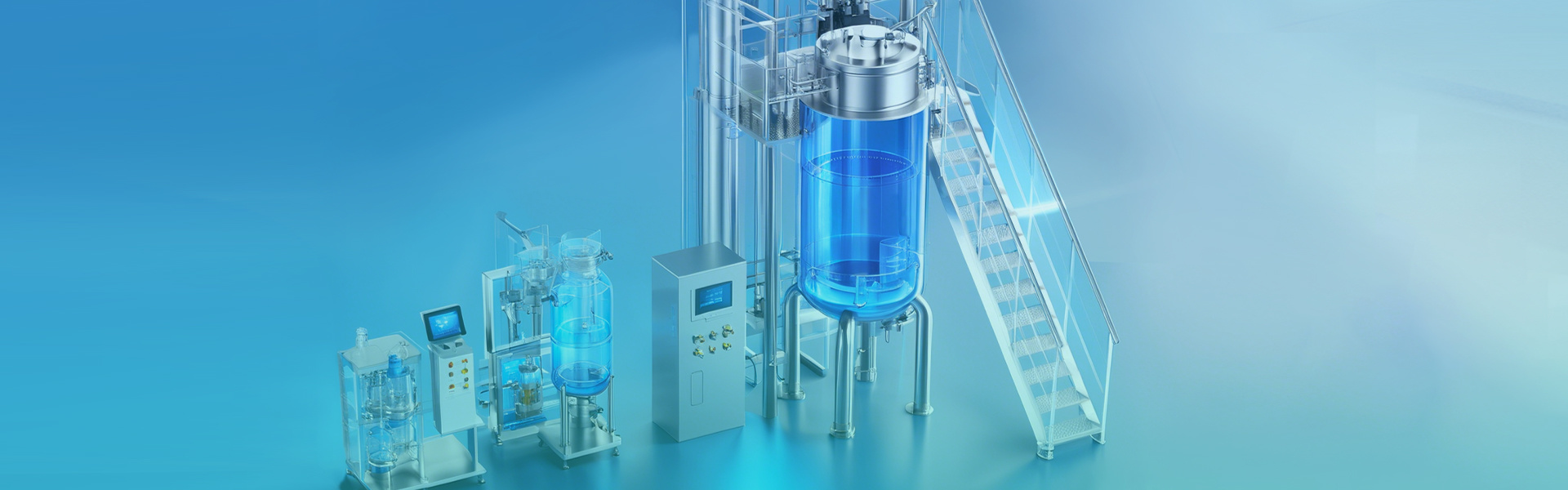
Bioreactors are widely used in the dairy, beverage bioengineering, pharmaceutical, and fine chemical industries. In terms of bioreactors, the commonly used fermentation tank equipment is mechanical stirring fermentation, and its sterilization effect directly affects whether fermentation can proceed normally. Its working principle is: using air nozzles to spray high-speed air, the air is dispersed in the liquid in the form of bubbles. On the aeration side, the average density of the liquid is reduced. On the unaerated side, the liquid density is higher, so there is a density difference with the aerated side liquid, thus forming a liquid circulation in the fermenter. There are many types of bioreactors, among which the common ones are inner circulation pipes, outer circulation pipes, tension pipes, and vertical baffles. The external circulation pipe is designed outside the tank body, and two inner circulation pipes are designed inside the tank body. In the bioreactor, the liquid level in the tank is not higher than the outlet of the circulation pipe and not lower than the circulation outlet. Bioreactors have advantages such as low energy consumption and less liquid frying. Under the same energy consumption, its oxygen transfer capacity is much higher than that of ordinary fermenters.
Let's talk specifically about the main advantages of bioreactors: 1. Bioreactors have a simple structure, the basic principle is not complicated, and the energy consumption is lower than that of a slurry reactor with a stirring paddle; 2. Relying on gas to generate directional circulation, instead of centrifugal pump mechanical equipment, its flow form is certain, the liquid circulation is strong, and there are no moving parts inside. The small shear stress and uniform energy dissipation are of great significance for shear-sensitive materials; 3. Compared with traditional fermenters, the flow range of gas and liquid in bioreactors is much larger. 4. Bioreactors have high gas supply efficiency, and the gas supply in the riser can be greater than that in the bubble reactor, which is beneficial to aerobic reactions; 5. Fluidization effect, it can be solid particles, even heavier particles are completely kept in suspension.
Of course, Bioreactors also have some Disadvantages: 1. Bioreactors require a very large air throughput; 2. Poor mixing and contact between each other; 3. When the circulating biology and operating conditions change, the amount of substrate, nutrients, and oxygen cannot be consistent; 4. Mixing and aeration are coupled problems, and it is difficult to improve mixing conditions without changing aeration.
Sterilization methods for bioreactors: 1. Before sterilizing the bioreactor, the air filter connected to the bioreactor should be sterilized with steam and dried with air. At the same time as the real tank sterilization, the sewage in the conveying pipeline is discharged and rinsed, and then the prepared medium is pumped into the fermenter, and the stirrer is started for sterilization at the same time. 2. Sterilization of bioreactors: First, open all exhaust valves and introduce steam into the jacket or coil for preheating. When the tank temperature rises to 80~90 ℃, remove the exhaust valve and slowly close it. Then, introduce steam into the fermenter directly from the air inlet, air outlet, and sampling port, so that the tank temperature rises to 118~120 ℃, and maintain the tank pressure of the fermenter at 0.09~0.1Mpa( gauge pressure ) ) within the range, maintaining 30 minutes or so. 3. Empty bioreactor sterilization refers to the sterilization of the bioreactor tank. Generally, the tank pressure is maintained at 0.15~0.2Mpa , and the tank temperature is at 125~130 ℃, maintaining 30 ~ 45 min ; the total steam pressure is required to be no less than 0.3~0.35Mpa , and the factory steam pressure is no less than 0.25~0.3MPa 。4. In-situ sterilization refers to sterilization without changing the tank structure during production, generally using online steam sterilization. Offline sterilization can be understood as removing the fermenter for sterilization, and small fermenters can be moved to a sterilization box for sterilization.
Latest News
2025-07-28
The 15th Shanghai International Bio-fermentation Products and Technology Equipment Exhibition 2025 will be grandly held at the Shanghai New International Expo Center from August 7th to 9th.
How can the fermentation system be upgraded?
2022-05-13
Fermentation systems are commonly used in research, production, seed production, and large-scale factory production units for liquid strains. They are also used in the cultivation of various microorganisms, the production of food containing edible fungal active ingredients, and the production of active factors in various dairy products. Therefore, its application range is very wide, commonly used in mycelia.
What are the disadvantages of laboratory fermenters?
2022-04-27
Laboratory fermenters are mainly used in research, production, seed production, and large-scale production units of liquid strains, and are also used in the cultivation of various microorganisms, the production of food containing edible fungus active ingredients, and the production of active factors in various dairy products. Therefore, its application range is very wide, usually in mycelia.
How is the fermentation system managed?
2022-04-21
Fermentation systems are used in the production of food and various dairy products' active factors, so their application is very widespread. Commonly used in mycelia, extracting bioactive ingredients to produce various food additives, extracting bioactive ingredients to produce various food additives, in microbial engineering it is used to produce pesticides, pharmaceuticals, hormones, etc., suitable for scientific research units, and mushroom companies.